If you think I'm a good fit for an open position or you just want to say hello, send a message! I look forward to hearing from you.
Purpose and Goal
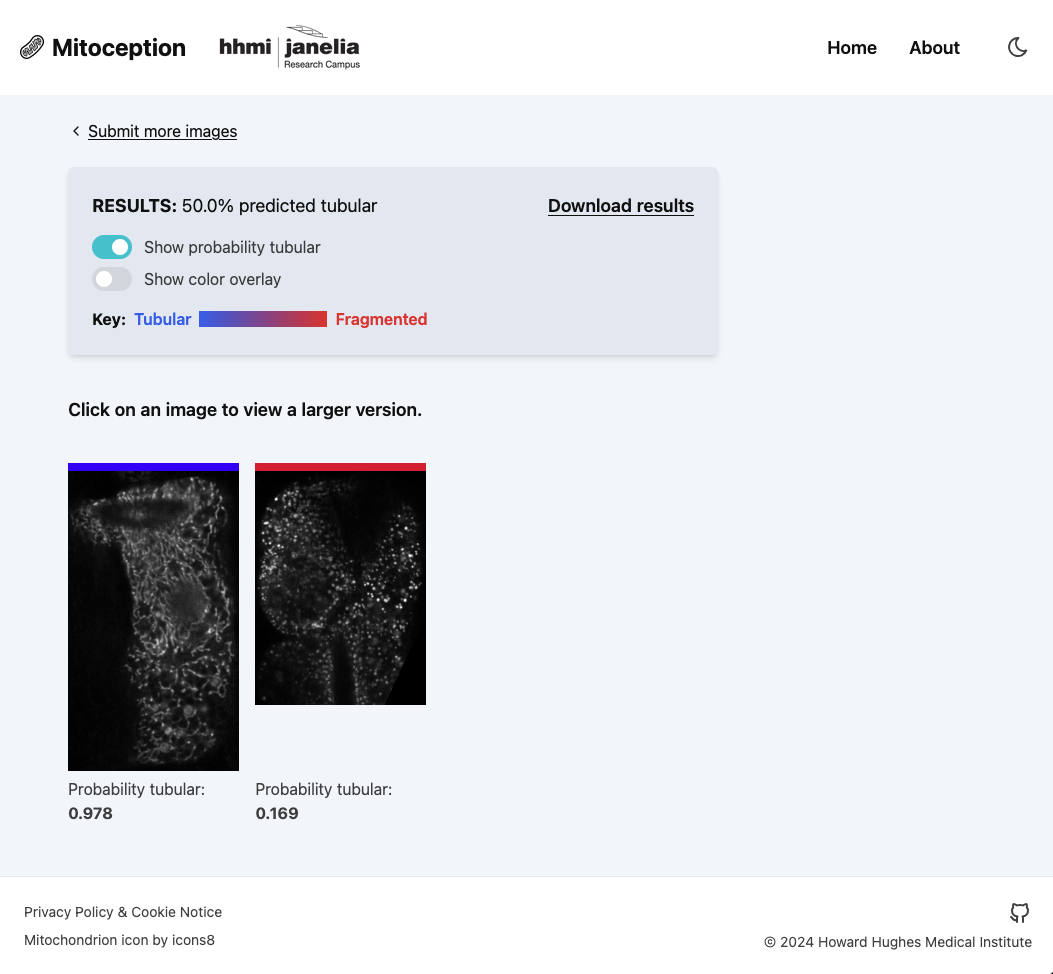
Mitoception is a web interface for image analysis using a machine learning model developed at Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Janelia Research Campus (Janelia). Researchers upload mitochondria images and receive back predicted classifications for the mitochondria structure.
My first implementation of the application used a FastAPI backend with PyTorch to perform inference on uploaded images. The new architecture gives the user the choice of using the server-based inference, or running inference entirely in the browser using WebAssembly. This achieves two goals: (1) minimizing concerns external users might have of submitting their data to Janelia servers and (2) reducing latency when there are many application users.
Spotlight: Implementing persistent model storage with IndexedDB
One of the primary challenges in migrating to client-side inference was managing the 28MB model file. Intially, the file was downloaded on every page refresh, resulting in delays of several seconds to over a minute depending on network conditions. This created an unacceptable user experience.
I implemented a caching solution using the browser's IndexedDB API to store the model file locally after the initial download. The implementation checks IndexedDB for an existing model before attempting to fetch from the server, and stores the model blob after successful download. This approach reduced model loading time from several seconds down to approximately 25 milliseconds on subsequent visits, dramatically improving the user experience.
The solution required careful coordination between React hooks and the WebAssembly runtime initialization sequence. I used a useEffect hook to trigger the model download and initialize the inference session when users first navigate to the analysis page. This also served to reduce the apparent latency because users needed time to select images, filling some to all of the time required for the initial download. Once initialized, I stored the inference session in React state for reuse across all subsequent analysis sessions. To handle the case where users might submit images before the model finished loading, I implemented a file queuing system that holds uploaded files in state and automatically processes them once the inference session is ready.
Current status
Mitoception is deployed in production but awaiting peer-review of the associated scientific publication before it is released for public use. The application supports batch uploads of up to 500 images and provides both visual results with color-coded probability overlays and downloadable CSV files for further analysis.



